2024-07-1113:42 Status:IBnotes
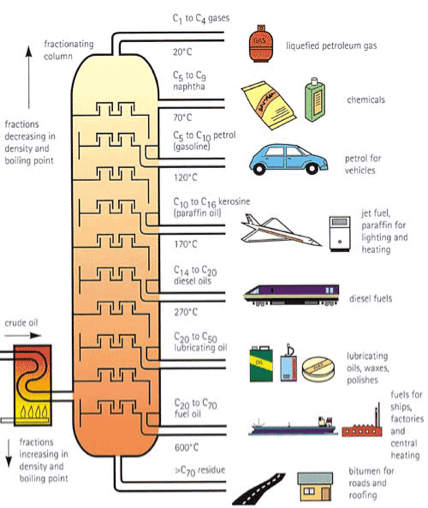
Fractional distillation
Crude oil (petroleum) is pumped directly from the ground. Wherein a complex mixture of all kinds of hydrocarbons can be refined and isolated physically and chemically. This is primarily done through fractional distillation: heating crude oil and materials then cooling them separately by their boiling points.
The smallest molecules rise to the top (as they are less dense, and have lower boiling points, rise faster, have fewer electrons and weaker LDF) And vice versa for larger molecules while they are also less flammable and volatile.
Solvent extraction
Solvent extraction is a physical process technique for separating organic materials from mixtures. A solvent is added to selectively dissolve and remove impurity, or separate some useful products from the mixture. This is how decaffeinated coffee is made.
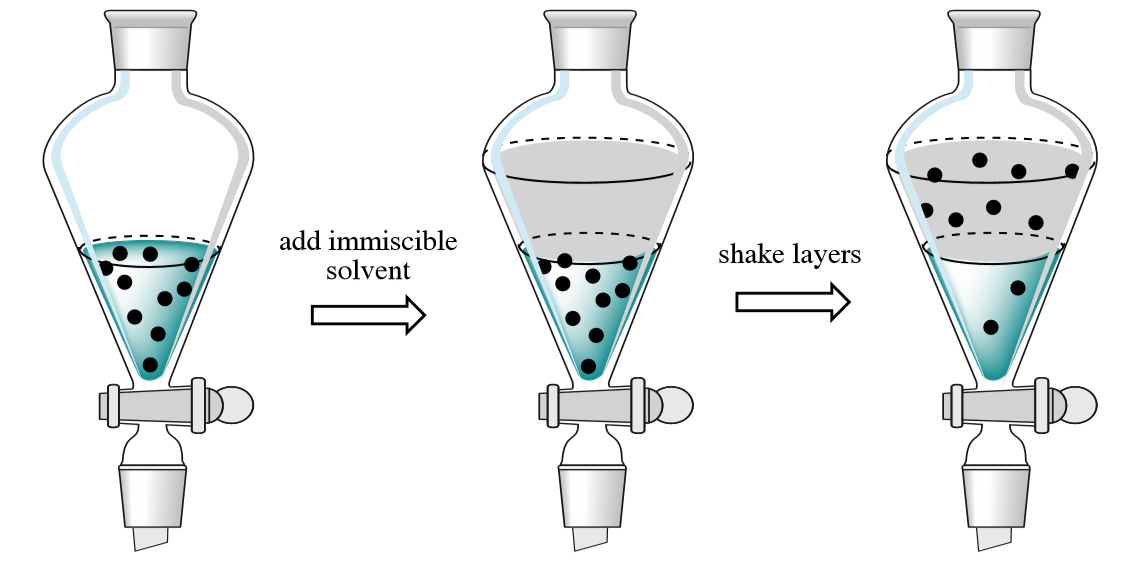
Solvent extraction is often used because there are not enough of the hydrocarbons in demand created from fractional distillation. Rocket fuel vs. plastic.
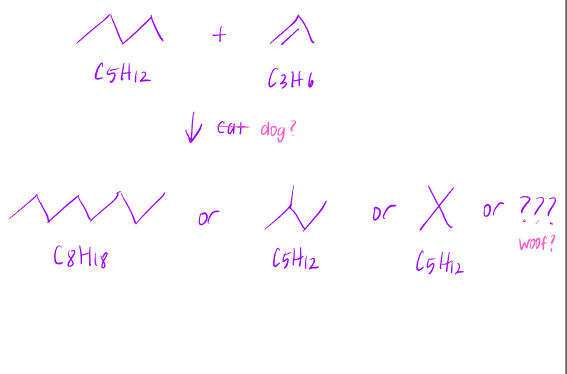
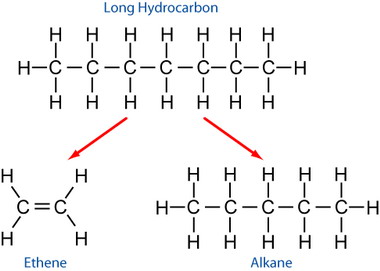
Cracking
Cracking is a type of reaction that takes a longer chain length fractions and further breaks it down to smaller molecules. For example: . This is the basis for petroleum refinement.
Because carbon and hydrogen must be conserved, at least one alkene will be formed.
Reforming
Reforming is a type of reaction that takes smaller molecules and reforms them. Thereby allowing for lower grade hydrocarbons (e.g. gasoline) into higher, larger grades of hydrocarbons (e.g. synthetic lubricants).